 press-releases
press-releases 
Radiation plays an essential role in diagnosing, monitoring, and treating an array of medical conditions. From X-rays and CT scans in medical imaging to radiation therapy for cancer, this energy form helps doctors understand their patients and deliver appropriate treatments. Explore a few interesting facts about medical radiation to learn more.
Radiology is a discipline that uses X-rays and other forms of high-energy radiation for medical imaging. In this setting, radiation helps doctors diagnose diseases and monitor treatments.
Radiology allows medical professionals to see conditions that are not immediately visible; for example, X-rays can show small bone fractures.
CT scans can produce detailed images of internal organs, allowing doctors to spot potential issues such as infections, tumors, and other abnormalities. By using radiation to create these images, doctors can detect and diagnose medical conditions early, leading to earlier treatments and improved outcomes.
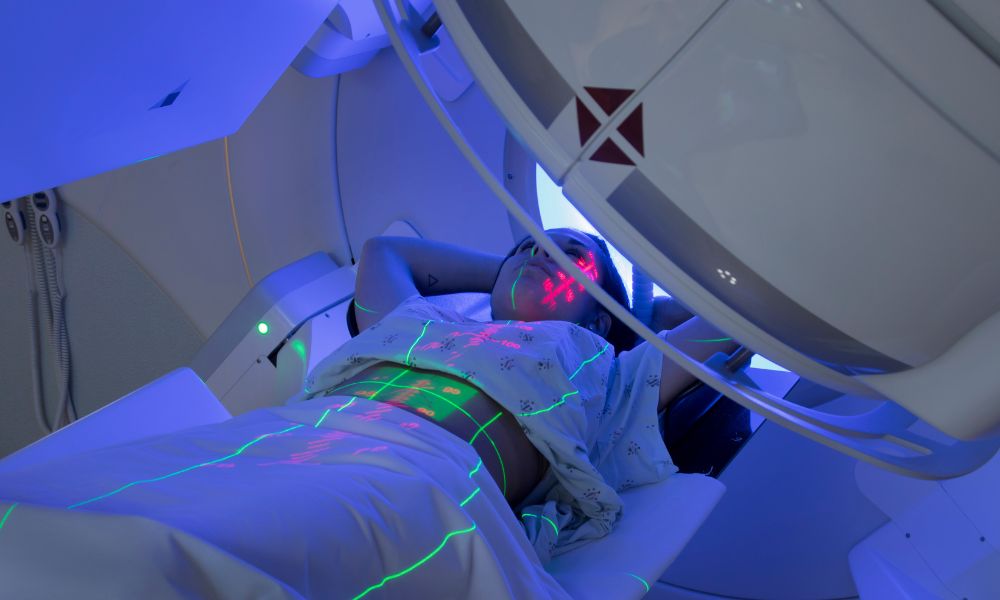
Another interesting fact about medical radiation is that radiation therapy for cancer can be administered internally or externally. External beam radiation therapy uses a machine that aims radiation energy at the cancer. External treatment addresses a specific part of the body.
Internal radiation therapy deposits radiation inside the body in solid or liquid form. Internal radiation with a solid radiation source provides local treatment to a specific body area, while liquid treatment travels in the blood to kill cancer cells throughout the body.
While medical radiation is a normal part of modern healthcare, medical professionals and patients must take specific precautions. There are various types of radiation exposure, but the kind of exposure that patients and personnel can experience from medical imaging differs from the exposure patients undergo when taking radioactive treatments. No matter the circumstances, patients and personnel must understand the risks and take protective measures.
Doctors follow strict guidelines and use the lowest possible radiation doses necessary to achieve desired results. Shielding devices, such as lead aprons, are also used to protect patients from unnecessary exposure during X-rays or CT scans.
24World Media does not take any responsibility of the information you see on this page. The content this page contains is from independent third-party content provider. If you have any concerns regarding the content, please free to write us here: contact@24worldmedia.com